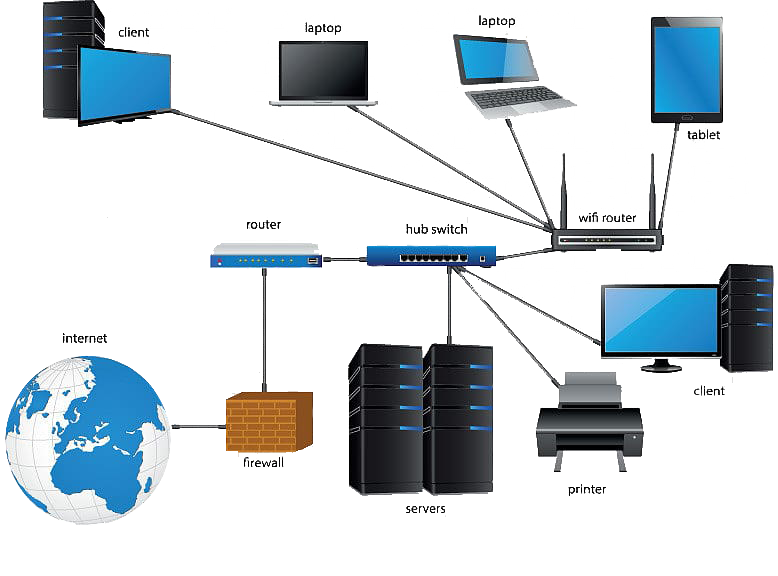
Data Network
In today’s digital world, the need to transmit and share information at faster speeds has become a vital necessity for many schools, businesses and large organizations. Communication networks are the systems used to share this information across different platforms such as email, video chat, voice, SMS, fax, etc. From confidential financial information to sensitive company information, the data you transfer on a daily basis ensures the successful operation of your business.
Every time you transport data to external devices, you place that information at risk. In order to reduce these inherent risks, you need a safe and reliable data network solution. That’s where we come in! At ITS Hawaii, we specialize in designing, implementing and supporting custom networking solutions that allows the transfer of your data assets safely and securely across multiple platforms and operating systems. However, before we get into what Data Networks we offer, let’s cover the basics:
What is Data Networking?
Data networking is the method by which our world stays connected. Through pre-defined routes and links, we are able to exchange data through our computers, telephones and mobile devices at the click of a button. Network routes can span across large geographical areas or can focus on a small network within a campus or office space. Through these data networks, messages are sent and eventually terminated in data center buildings that house the hardware to power the network. Depending on your specific security needs, these routes may be private systems, public systems or a combination of the two and with the ever-increasing expansion of businesses and networking capabilities, additional lines are usually needed in order to support more devices and locations. These increased demands are now requiring more connectivity, larger bandwidth for data transmission and increased security to protect information from unauthorized access. As more complex data, such as larger video files and more secure information from corporations, continues to increase, businesses are finding new ways to build larger, higher performing and overall more secure networks.
Common Data Network Solutions
There are a host of data networks. Below you will find a list of the types of data networks we work with and a little about what each network entails:

Personal Area Network (PAN)
Learn More
Typically found in small offices or residences, a PAN is the smallest and most basic type of network. PAN’s are usually managed by one person or organization in a single building and are made up of a wireless modem, one or two computers, phones, printers, tablets, etc. that are connected to a single device.

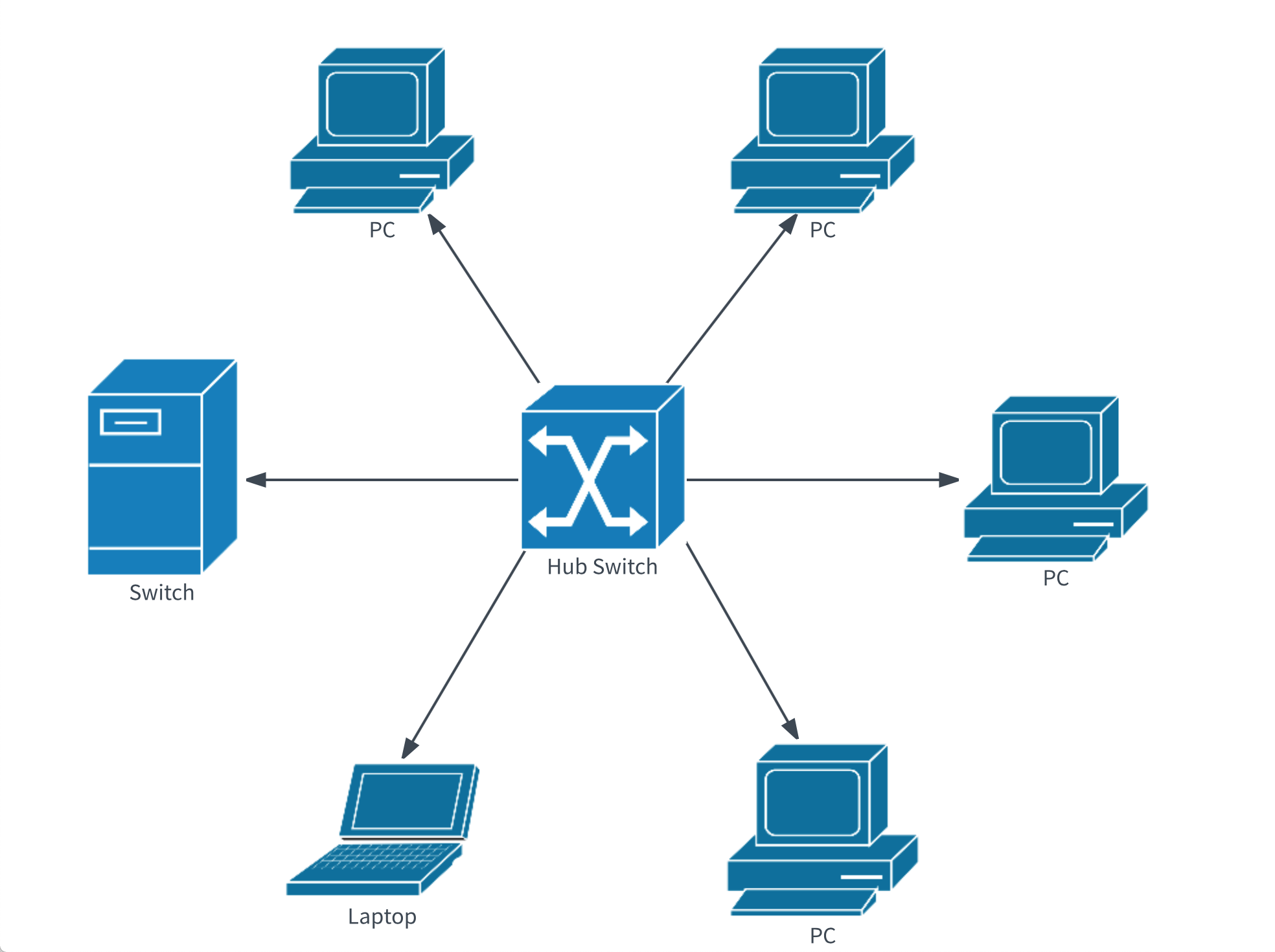
Local Area Network (LAN)
Learn More
LAN’s are the most common and well-known data networking options available. As a simple data network, LAN’s connect groups of computers and low-voltage devices together across very short distances – usually within a building or between a group of several buildings that are within a close proximity to one another. These types of networks allow devices to share information and resources and are most commonly utilized by enterprises. Through the use of routers, LAN’s can connect to a wide area network (or WAN) for the rapid and safe transfer of data.

Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
Learn More
Similar to LAN’s are WLAN’s which typically use the same applications as LAN. These data networks make use of wireless technology, like Wi-Fi. Contrastingly, however, these types of networks do not rely on physical cables and instead utilize wireless network technology to connect to devices.


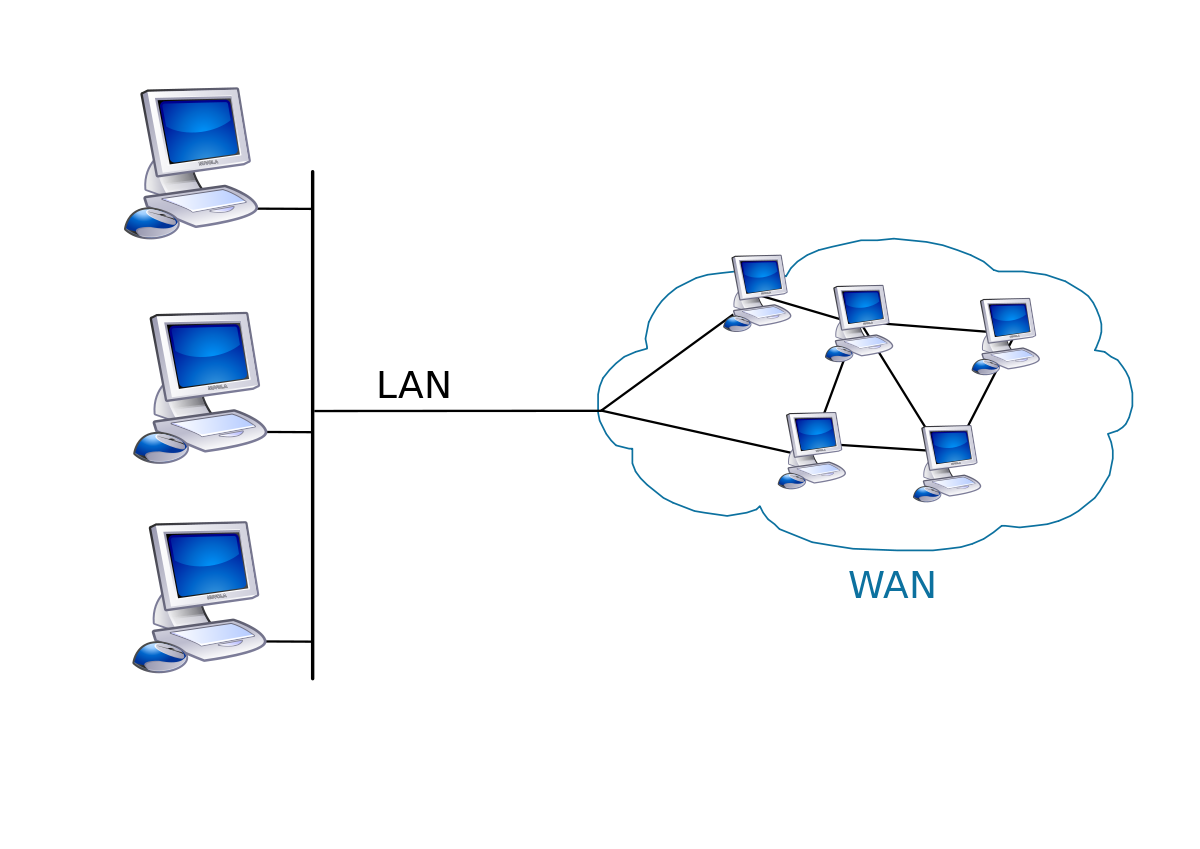
Wide Area Network (WAN)
Learn More
A WAN is slightly more complex than a LAN and covers a large geographic area. This type of network usually consists of multiple computer networks or a number of low-voltage devices which are remotely connected over one large network – allowing users to communicate even when miles apart. WAN’s utilize routers, switches, modems and servers to provide connectivity to workers and organizations around the globe. The internet is the most common example of a WAN is the internet as it connects computers around the world. Due to it’s vast reach, WAN’s are typically owned and managed by multiple administrators.

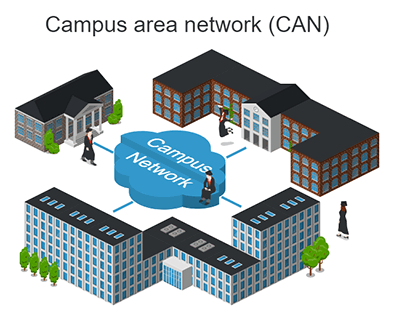
Campus Area Network (CAN)
Learn More
CAN’s are larger than LAN’s but work in virtually the same way. A Campus Area Network are most commonly used in universities, large K-12 school districts and small businesses. Utilizing multiple interconnected local area networks in a limited geographical area, CAN’s can be spread across several buildings that are fairly close so users can share resources. This type of network is also known as Corporate Area Network since it is used in small corporations as well.

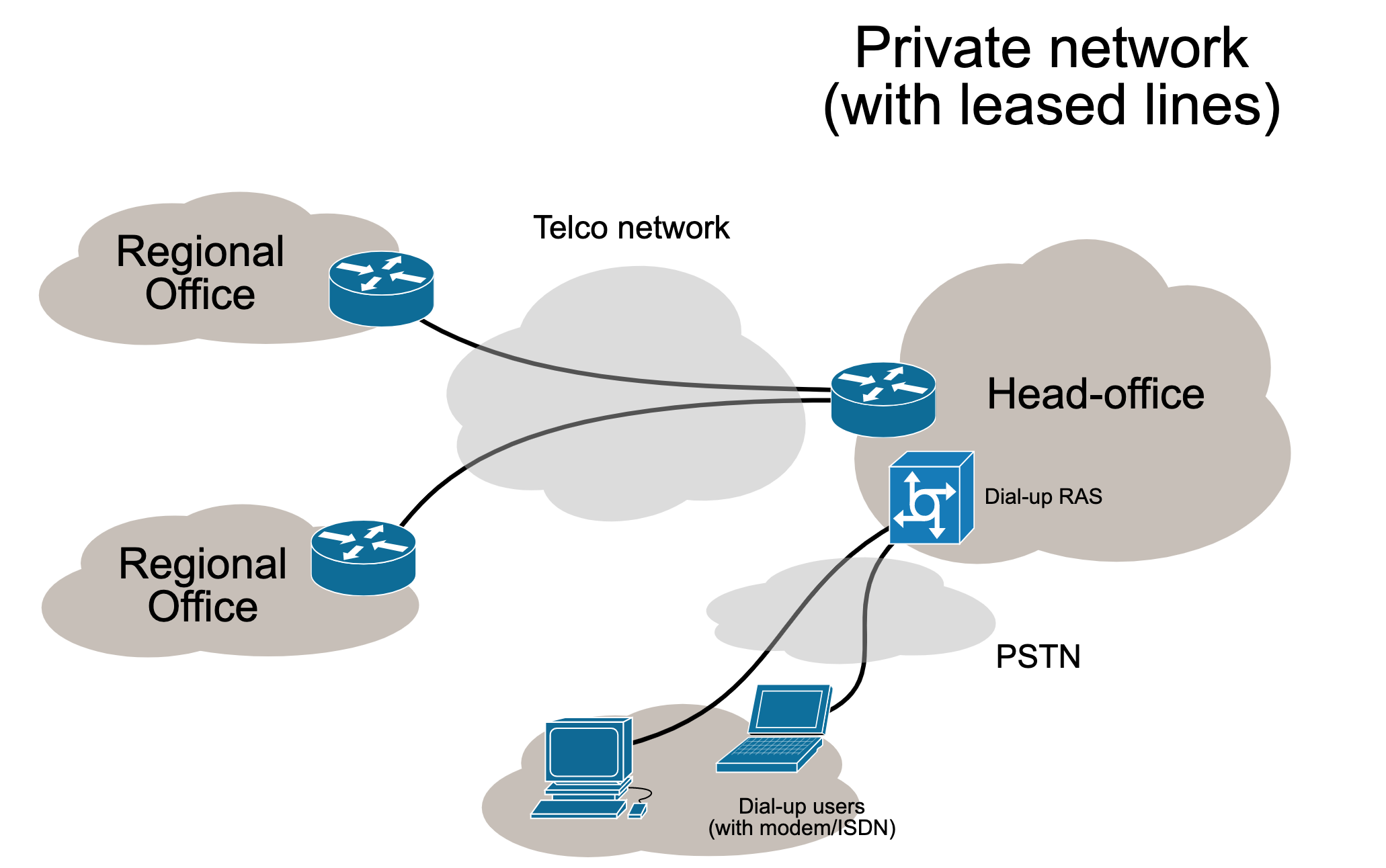
Enterprise Private Network (EPN)
Learn More
Enterprise Private Networks are computer networks built by a business to connect various company sites in order to share resources. These types of networks are typically built and owned by businesses that want to securely connect multiple locations such as production sites, corporate offices and shops.

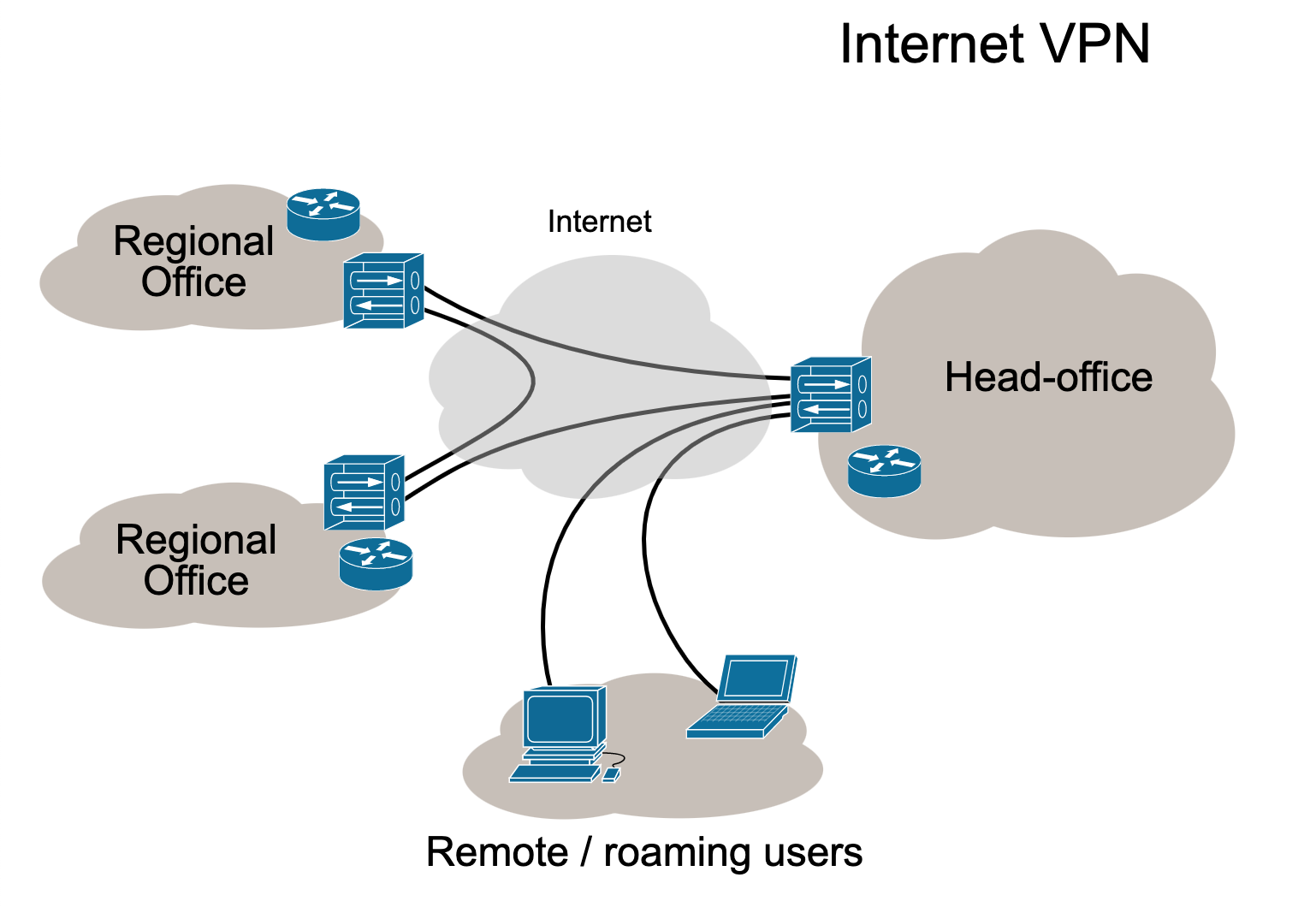
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Learn More
Virtual Private Networks allow users to connect to the internet through an encrypted portal in order to protect sensitive data and ensure online privacy. VPN’s are typically used to secure connections to public Wi-Fi hotspots, hide IP addresses and making online browsing private. VPN’s also allow users to send and receive data as if their devices were connected to the private network – allowing access to private data more securely using a point-to-point connection.

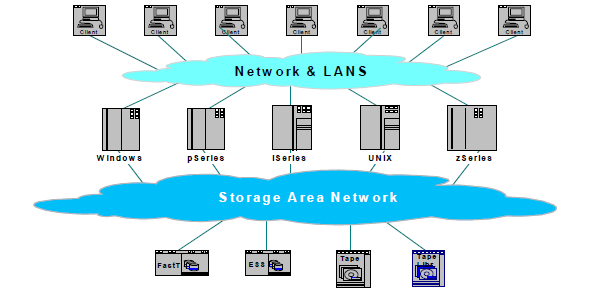
Storage Area Network (SAN)
Learn More
Although SAN’s was most widely used by larger companies, recent findings have shown that a growing number of small companies are starting to incorporate these types of networks. SAN’s are high-speed networks that don’t rely on a LAN or WAN and connect data storage tools with larger networks. They are used to facilitate communication between computer systems and other networks using SAN switches to connect to pools of storage. They do this by moving torage resources away from the network and placing them into their own high performance network. The storage pool is then managed, maintained and controlled by administrators who assign logical unit numbers (LUNs) or blocks of storage capacity. SANs can be accessed the same way an external drive can be attached to a server.

System Area Network (also SAN)
Learn More
SAN’s are an up and coming type of network that has gained popularity in the last decade. This type of network is descriptive of a high performance, connection oriented network that can link a cluster of computers. SANs are designed to provide high-speed connection, deliver high bandwidth of 1Gbps or greater with low latency. Unlike existing networks such as Ethernet and ATM, a SAN offers a reliable transport service that guarantees uncorrupted data in the same order in which it was sent.